In general, a variable is a named entity that can hold a value or information.
It act as a placeholder to store data that can be accessed, modified and manipulated with a program or a block.
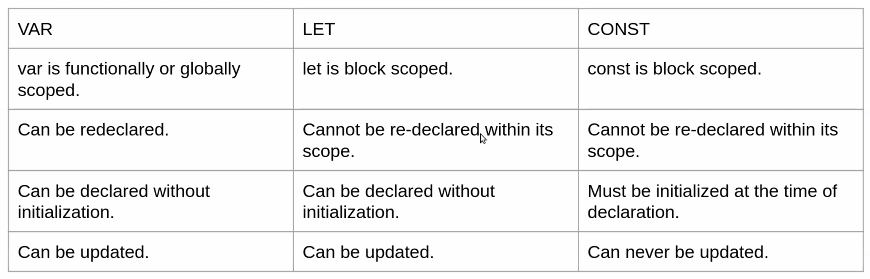
Declaring Variable:
In JavaScript, variable are delared using the
- var
- let
- const
Keywords.
For example
var myVariable;
let anotherVariable;
const constantVariable = 10;
Variable Types:
JavaScript has two main types of variables:
- primitive data types
- Number
- String
- Boolean
- Null: Represent the absence of any object value.
- Undefined: Represent the absence of a defined value.
- Reference data types
- Object: Represents a collection of key-value pairs.
- Array: Represents an ordered list of values.
- Function: Represents reusable code blocks
- and more…
Variable Scope:
Variable in JavaScript have either global or local scope.
Global Scope:
Variable declared outside of any function have global scope. They can be accessed from anywhere in the code.
Local Scope
Variables declared within a function have local scope. They can only be accessed within the function or nested functions.
Conclusion
Understanding JavaScript variables is crucial for any JavaScript developer. They provide the means to store, retrieve, and manipulate data dynamically. By grasping the concepts covered in this blog post, you’re equipped with the foundation needed to handle variables effectively in JavaScript.