Distributing user traffic across instance of an application in single region or multiple regions.
- Fully distributed, Software defined managed service
- Features:
- Health checks – Route to healthy instances
- Recover from failures
- Auto scaling
- Global load balancing with single anycast IP
- Also support internal load balancing
- Health checks – Route to healthy instances
Terminology
Backend: Group of endpoints that receive traffic from a Google Cloud load balancer (Example: Instance groupd)
Frontend: Specify an IP address, port and protocal. This IP address is the frontend IP for your clients requests
- For SSL a certificate must also be assigned.
Host and path rules (For HTTP(s) Load Balancing) – Define tules redirecting the traffic to different backends:
- Based on path – example.com/a vs example.com/b
- Based on Host – a.exmaple.com vs b.example.com
- Based on HTTP headers (Authorization header) and methods (POST, GET, etc)
SSL/TLS Termination/Offloading
- Client to load Balancer: Over internet
- HTTPS recommended
- Load Balanacer to VM instance: Through Google internal network
- HTTP is ok. HTTPs is preferred
- SSL/TLS Termination/Offloading
- Client to Load Balancer: HTTPs/TLS
- Load Balancer to VM instance: HTTP/TCP
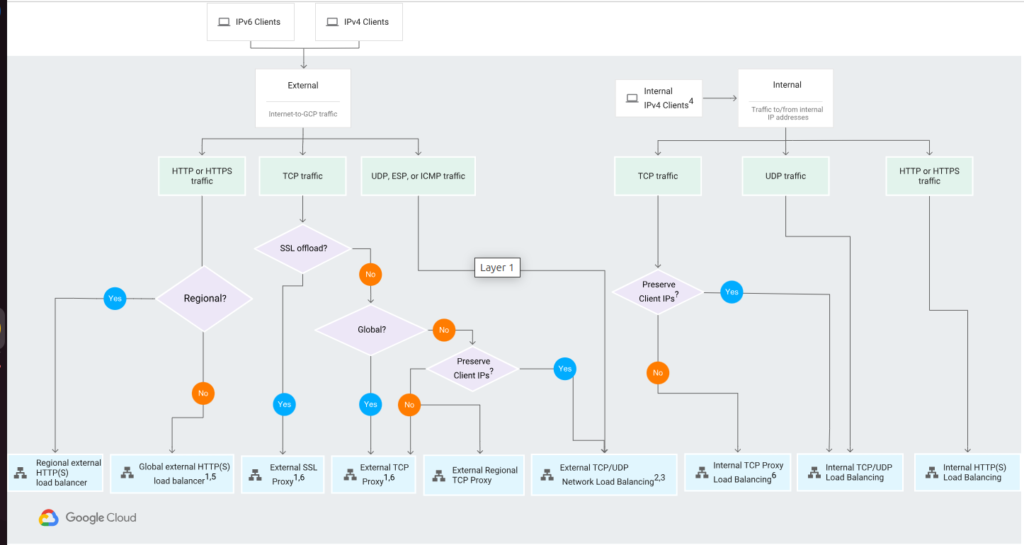
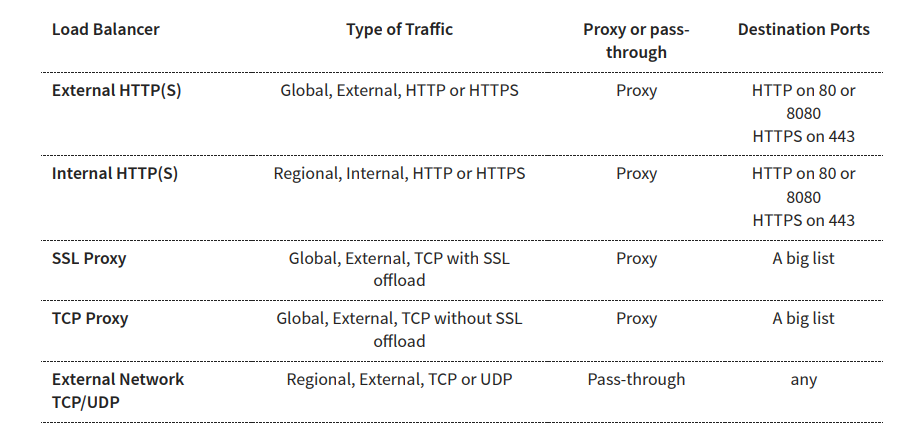
Choosing Load Balancer