Managed services refer to the practice of outsourcing the responsibility for maintaining and managing IT systems and infrastructure to a third-party provider.
Terminology
- IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
- PaaS (Platform as a Service)
- FaaS (Function as a Service)
- Caas (Container as a Service)
- Serverless
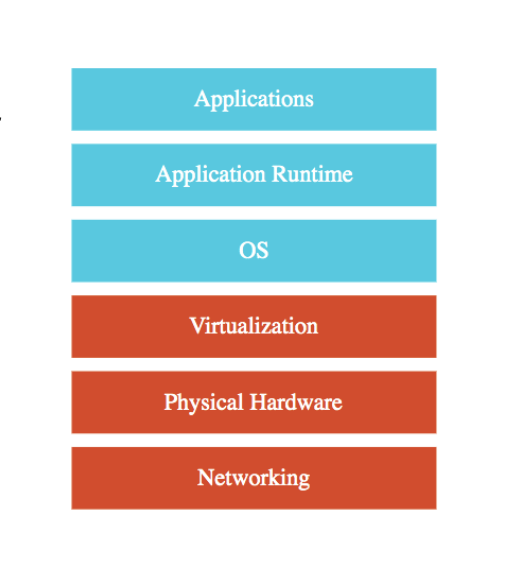
IAAS (Infrastructure as a Service)
Using VM to deploy your applications or database. GCP provide infrastructure.
You are responsible for :
- Application Code and Runtime
- Configuring load balancing
- Auto scaling
- OS upgrades and patches
- availablity
- etc…
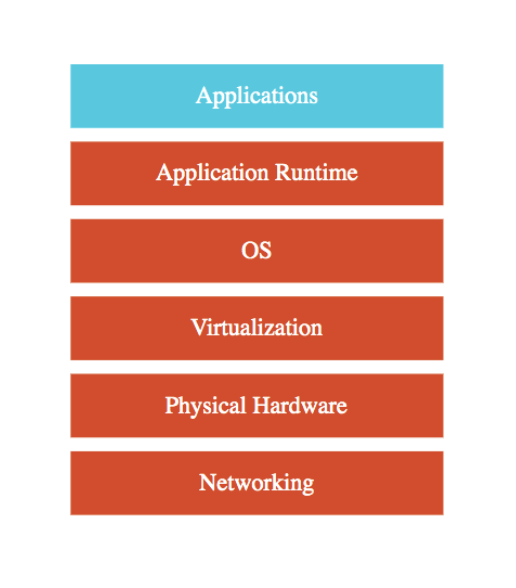
PAAS (Platform as a Service)
Use a platform provided by cloud
GCP is responsible for:
- OS (incl. upgrades and patched)
- Application Runtime
- Autocaling, Availablity & Load balancing etc…
User is responsible for:
- Configuration (of application and services)
- Application code (If needed)
Varieties:
- CAAS (Container as a Service): Containers instead of Apps
- FAAS (Function as a Service): Function instead of Apps
- Database – Relational & NoSQL (Amazone RDS, Google Cloud SQL, Azure SQL Database etc), Queues, AL, ML, Operations etc!
Microservices
a microservice is a small, independent, and loosely coupled service that is part of a larger application. It typically runs in its own container or cloud service and communicates with other services through APIs.
Enterprises are heading towards microservices architectures
- Buildign small focus microservices
- Flexibility to innovate and build application is different programming languages(Go, JAVA, Python, JavaScript, etcs)
But Depoyments become complex!
Using containers we have one way of deploying Go, Java, Python or JavaScript in Microservices.
Containers – Docker
Docker is an open-source platform for developing, shipping, and running applications inside lightweight, portable containers. It enables developers to package an application and its dependencies into a single container that can run anywhere—on a local machine, cloud, or server.
Container Orchestration
Container orchestration is the process of automating the deployment, management, scaling, and networking of containerized applications. It ensures that multiple containers work together efficiently, making it ideal for microservices architectures.
Why Do We Need Container Orchestration?
✅ Automated Scaling – Adds or removes containers based on traffic
✅ Load Balancing – Distributes traffic among containers
✅ Self-Healing – Automatically restarts failed containers
✅ Efficient Resource Management – Optimizes CPU & memory usage
✅ Service Discovery & Networking – Manages communication between containers
Serverless
Serverless computing in Google Cloud Platform (GCP) allow you to build and deploy application with managing servers. GCP automatically handles infrastructure, scaling, and maintenance, so you can focus on writing code.
Serverless Services in GCP
| Service | Use Case | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Cloud Functions | Event-driven execution | Runs small code snippets in response to triggers (HTTP, Pub/Sub, etc.) |
| Cloud Run | Deploy containerized applications | Fully managed, supports any language, auto-scales |
| App Engine | Deploy web applications & APIs | Supports multiple runtimes, built-in scaling |
| Firestore | Serverless NoSQL database | Real-time sync, highly scalable |
| Pub/Sub | Event-driven messaging | Asynchronous messaging for microservices |
| Cloud Tasks | Asynchronous background jobs | Manages task queues with retry logic |
| BigQuery | Serverless data warehouse | Processes large datasets using SQL |
Choosing the Right Serverless Service in GCP
| Use Case | Best Serverless Option |
|---|---|
| Run event-driven functions | Cloud Functions |
| Deploy containerized microservices | Cloud Run |
| Host web apps and APIs | App Engine |
| Process real-time streaming data | Pub/Sub + Cloud Functions |
| Query large datasets | BigQuery |