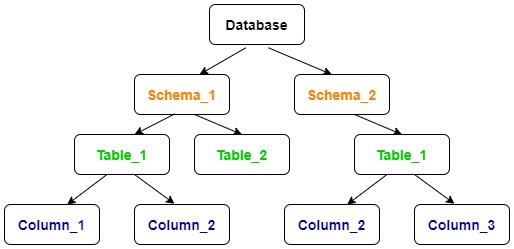
As the above image represents “Database vs Schema vs Table,” these are the fundamental hierarchy in a PostgreSQL (and most relational) database system.
1. Database
The Database is the largest container that holds an entire collection of data and its structure. It’s2. an isolated environment where all your related data is stored.
2. Schema
A Schema is a logical container that exists inside a database. It acts as a namespace to organize related database objects like tables, views, and functions.
- Role: Organizes objects into logical groups, It’s like a folder within a database.
- Namespace: It solvess naming conflicts. You can have a
userstables in a billing schema and another useruserstable in an auth schema within the same database e.g.,billing.usersandauth.users).
3. Table (The Individual Files/Spreadsheets)
A Table is the core object used to store the actual data. It resides inside a schema.
- Role: Stores the data in a structured format of rows (records) and columns (attributes/fields).
- Structure: The structure of a table is defined by its columns, each with a specific name and data type (e.g.,
VARCHAR,INTEGER,DATE).